When your furnace fails to heat your home on a cold Metro Atlanta day, the discomfort and urgency can be overwhelming—but before calling for service, several common, fixable issues may be the culprit. From a tripped circuit breaker and dirty air filter to a malfunctioning thermostat or faulty pilot light, understanding how to troubleshoot basic problems can restore warmth quickly and potentially save you from an unnecessary service call. In this guide, we’ll walk Metro Atlanta homeowners through a logical, step-by-step troubleshooting furnace not heating process to diagnose why your furnace isn’t heating and determine when it’s time to call in a professional.
Troubleshooting Furnace Not Heating Issues Homeowners Face Most
What Safety Precautions Should You Take Before Troubleshooting Your Furnace?

Before you do any work on a furnace that is not producing heat, safety comes first. Many common steps for troubleshooting furnace not heating issues involve getting close to electrical components, gas lines, and moving parts. Taking a few minutes to secure the area and shut things down properly reduces the risk of shocks, burns, and gas leaks while you work.
Start by turning off the power to the furnace at the dedicated switch or breaker. Most units have a nearby service switch that looks similar to a light switch. Flip this off, then verify that the blower and control board are no longer running. For extra peace of mind, it is a good idea to also shut off the furnace breaker at the main panel so you are not working around live power while you inspect panels or wiring.
Once the power is off, turn your attention to the gas supply. Locate the gas shutoff valve on the supply line to the furnace and rotate it to the off position so the handle sits perpendicular to the pipe. This step matters even if you are only planning a quick visual check. If you smell gas at any point, do not continue troubleshooting furnace not heating problems on your own. Leave the area, ventilate if it is safe to do so, and contact your gas company or a licensed HVAC technician.
Make the work area as safe and comfortable as possible. Clear clutter away from the front and sides of the furnace so you have a solid footing and room to remove access panels. Keep children and pets out of the area while you work. Wear basic protective gear such as safety glasses and work gloves, especially if you will be brushing away dust or reaching into tight spaces where sheet metal edges are exposed.
Before you begin any hands-on checks, take a moment to review the furnace’s user manual if you have it. The manual often includes model-specific safety warnings and diagrams that show where switches, sensors, and filters are located. Knowing what you are looking at reduces the temptation to guess or to bypass safety features, both of which can create bigger hazards than the original problem.
Why Checking Carbon Monoxide Detectors Is Essential
Any time you are dealing with a gas furnace, carbon monoxide safety should be part of your routine. A furnace that is not burning fuel cleanly can release carbon monoxide into the home, so it makes sense to confirm that your monitoring devices are working before and after you work on the system.
Test each carbon monoxide detector by pressing the test button and waiting for the alarm tone. If the unit does not sound, replace the batteries and test again. Detectors also have a service life, often around 7 to 10 years, so check the manufacture date on the back and replace any units that are past their marked life span. Place detectors in or near sleeping areas and on each level of the home for better coverage.
Pay attention to physical symptoms as well. Headache, dizziness, nausea, or confusion that improve when you step outside could indicate a carbon monoxide problem. If alarms ever sound while the furnace is running, get everyone out of the house, call emergency services, and do not attempt to restart or continue troubleshooting furnace not heating issues until the system has been inspected by a professional.
By combining basic shut-off steps, a tidy work area, and functioning carbon monoxide detectors, you create a safer setting for any basic checks you plan to perform. Even if you ultimately decide to call an HVAC company, starting with these precautions protects your household and gives a clearer picture of what might be going wrong with your furnace.
How Can You Troubleshoot Common Furnace Issues Yourself?
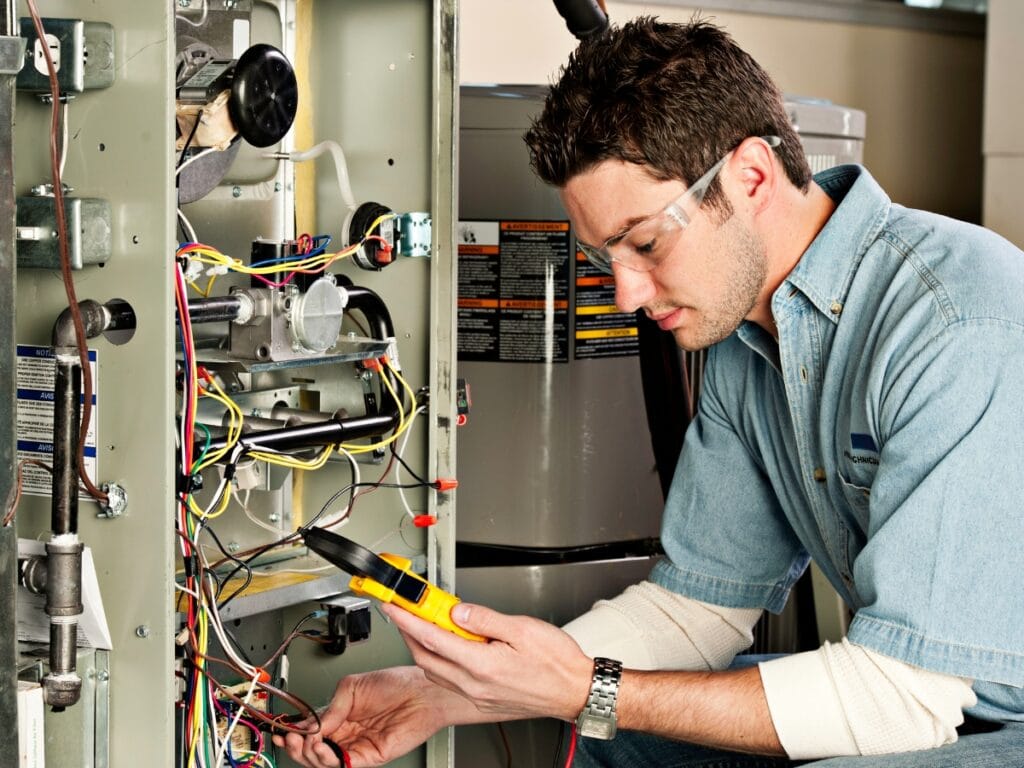

When the heat cuts out, it is easy to assume something major has failed, but many problems turn out to be simple fixes. Before you call in a professional, there are a few safe checks you can do on your own that often restore normal operation. Basic steps like confirming thermostat settings, checking the air filter, and making sure the system has power can go a long way when you are troubleshooting furnace not heating problems.
How To Check And Adjust Your Thermostat Settings
Start with the thermostat, since it is the control center for your heating system. Make sure it is set to “Heat” and not “Cool” or “Off.” Then confirm that the set temperature is higher than the current room temperature. If the display is blank, dim, or flickering, replace the batteries if your thermostat uses them. A weak battery can cause the furnace to cycle irregularly or not come on at all.
If you have a programmable or smart thermostat, review the schedule to see whether it has been changed recently. A weekday or vacation schedule can override what you think you set, so double-check that the current time and day are correct and that no setback temperatures are keeping the home cooler than you expect. After you make changes, wait several minutes to see if the furnace responds, as many systems have a short delay built in.
These simple thermostat checks are often enough to fix basic comfort issues and should always be part of troubleshooting furnace not heating situations.
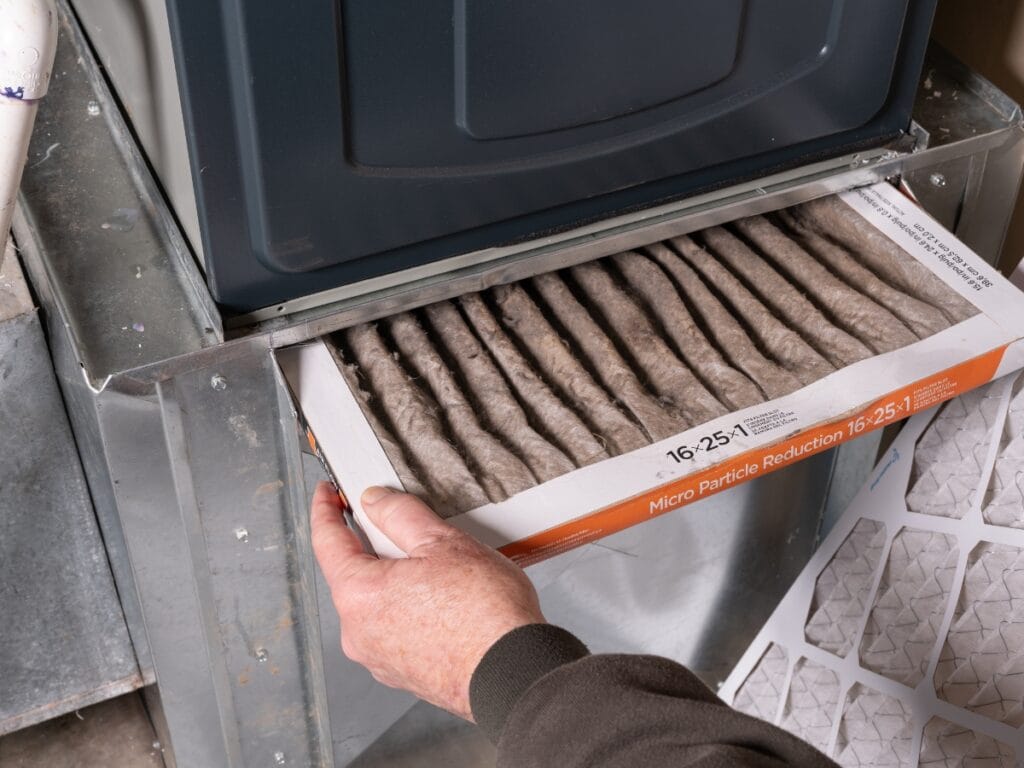
When And How To Inspect Or Replace Your Furnace Air Filter
If the thermostat looks fine, turn your attention to the furnace air filter. A clogged filter restricts airflow, which can cause weak heat output, short cycling, or even a safety shutdown if the system overheats. Locate the filter compartment, usually near the return air duct or inside the blower compartment, and slide the filter out carefully so you can examine it.
Hold the filter up to a light source. If little to no light passes through or the surface looks heavily coated in dust and debris, it is time for a replacement. Most homes do well with changing filters every one to three months, but homes with pets, smokers, or ongoing renovation work may need more frequent changes. Always match the size printed on the existing filter and choose a quality filter that your system can handle without restricting airflow too much.
After installing the new filter with the airflow arrow pointing in the correct direction, restore power to the furnace if you turned it off and see whether the airflow and heat output improve over the next heating cycle. Keeping up with this one task protects components, maintains efficiency, and prevents many common performance complaints.
Additional Simple Checks Before Calling A Professional
If thermostat and filter checks do not solve the problem, there are a few more quick things you can safely review. Confirm that the furnace switch near the unit is in the “On” position and that the corresponding breaker in the electrical panel has not tripped. Reset a tripped breaker once; if it trips again, stop there and contact a licensed HVAC technician.
Walk through your home and open any closed supply registers, and make sure return grilles are not blocked by furniture, rugs, or boxes. Restricted airflow in the living space can make it seem like the furnace is not heating even when it is running.
These basic steps will not fix every issue, but they often resolve the most common causes of a furnace that is not keeping up. They also give you useful information to share with a technician if you need professional help, making the rest of the troubleshooting process faster and more accurate.
What Steps Should You Take To Verify Your Furnace’s Power Supply?

When you are troubleshooting furnace not heating problems, one of the first things to confirm is that the system actually has power. Furnaces depend on a steady electrical supply for ignition, the blower motor, and safety controls, so even a simple power issue can leave the system completely unresponsive. Before you assume there is a major mechanical failure, it is worth taking a few minutes to check the switch, breaker, and any obvious electrical concerns so you can rule out the basics.
How To Check The Furnace Switch And Circuit Breaker
Start by locating the furnace switch, which is usually mounted on a nearby wall or right on the side of the unit. It often looks like a standard light switch, so it is easy for someone to turn it off accidentally while working or cleaning. Make sure it is fully in the “on” position, then give the system a few minutes to respond, since some furnaces have a short delay before they start up.
If the switch is already on, move to your home’s main electrical panel. Look for the breaker labeled for the furnace or air handler. A tripped breaker may sit in a middle position or clearly show as “off.” Flip it firmly to the off position and then back on to reset it. Only reset a breaker once. If it trips again quickly, leave it off and do not continue cycling it. Repeated tripping points to a deeper electrical problem that needs a professional, and forcing it can create a safety hazard.
These two quick checks often resolve a completely dead furnace and are an important part of troubleshooting furnace not heating complaints before you move on to more complex causes.
How To Spot Electrical Issues That Affect Furnace Operation
If the switch and breaker both appear normal and the furnace still does not respond, pay attention to other signs of electrical trouble in the home. Flickering lights when the furnace tries to start, outlets that seem unreliable, or a faint buzzing noise from the unit can all suggest wiring or control problems rather than a simple power interruption. You may also notice the blower starting and stopping repeatedly without producing warm air, which can indicate control board or safety circuit issues.
At this point, it is safer to stop your own troubleshooting and call a licensed HVAC technician or electrician. Internal furnace wiring, control boards, and high voltage components should not be opened or tested without proper training and tools. A professional can measure voltages, check connections, and test individual parts without putting your home or your safety at risk.
By working through this sequence in order, you cover the most likely power-related causes first and gather useful information if you do need expert help. Confirming power at the switch and panel, watching for clear electrical warning signs, and knowing when to stop all fit into a practical, step-by-step approach to keeping your furnace reliable and your home comfortable.
How Do You Inspect And Relight The Pilot Light Or Check The Ignition System?

When you are troubleshooting furnace not heating issues, it helps to know whether your system uses a standing pilot light or an electronic ignition. Many older gas furnaces still rely on a small, constant flame, while newer models typically use spark or hot-surface igniters that light only when the thermostat calls for heat. Before you touch anything, make sure the power to the furnace is off at the switch and that the area is well ventilated.
Start by removing the burner access panel so you can see the burner area. If your furnace has a pilot light, you will see a small metal tube leading to a tiny burner in front of the main burners. For electronic ignition, you will usually see a small rod or ceramic igniter near the burner instead of a standing flame. As you work through troubleshooting furnace not heating problems, simply observing what happens when the thermostat calls for heat can give you useful clues. For example, repeated clicking with no flame often points to an ignition problem, while a furnace that does nothing at all may have a power, limit switch, or control issue.
What Are The Signs Of Pilot Light Or Ignition System Failure?
A pilot light or ignition problem often shows up long before the furnace stops working completely. If you do have a standing pilot, pay attention to how the flame looks. A healthy pilot flame is steady and mostly blue, with only a small yellow tip. A flame that is mostly yellow, very weak, or blowing around suggests a problem with airflow, dirt in the orifice, or gas supply to the pilot.
Intermittent heating is another common warning sign. If the furnace starts, runs briefly, then shuts down and tries again, the flame sensor or ignition control may be struggling to prove a stable flame. You might also hear repeated clicking without ignition, see the burners light and go out quickly, or notice that the blower runs with no warm air coming from the vents. Any smell of gas that does not clear quickly is a red flag; in that case, leave the area and contact your gas company or a licensed technician rather than continuing to troubleshoot on your own.
Safe Procedures For Relighting A Pilot Light
If your furnace uses a pilot and it has gone out, you can often relight it safely as long as you follow the instructions on the appliance and take your time. First, turn the thermostat down so the furnace is not calling for heat. Set the gas control on the furnace to the “off” position and wait at least five minutes so any residual gas can dissipate. This waiting period is important for safety and should not be skipped.
After the wait, locate the lighting instructions printed on or near the furnace. Turn the control knob to “pilot” and press it down to start the gas flow to the pilot assembly. While holding the knob down, use a long match or a long-neck lighter at the pilot burner until the pilot lights. Keep holding the knob for another 20 to 30 seconds so the safety sensor can warm up. Then release the knob and turn it to “on.” Finally, restore power at the switch and turn the thermostat back up to see if the main burners light and stay on.
If the pilot will not stay lit after one or two careful attempts, or if you feel unsure at any point, stop and bring in a professional. For furnaces with electronic ignition, homeowners should limit themselves to basic checks such as power, filters, and thermostat settings; the ignition components themselves are not a safe DIY repair. Respecting these limits keeps you safe while still allowing you to do practical, informed checks before scheduling service. help you relight your pilot light without incident.
How Can You Identify and Resolve Airflow and Ventilation Problems?
When you are troubleshooting furnace not heating issues, airflow is one of the first things to check. Even a healthy furnace cannot heat your home properly if warm air cannot move through the ducts and out of the registers. Poor airflow can make some rooms feel chilly while others are comfortable, and it can force the system to run longer than it should, which adds wear and raises utility bills.
Start with a walk through your home and pay attention to how each vent feels. If some rooms have weak airflow or noticeably cooler air, that can point to a partially closed register, a blocked grille, or a duct problem. Furniture, rugs, and curtains often end up over supply or return vents, which restricts circulation without anyone noticing. As part of a basic home security and comfort routine, it is worth checking all visible vents at the beginning of each heating season to confirm that they are open, uncovered, and free of dust buildup.
You should also pay attention to how the system behaves as a whole. A furnace that cycles on and off frequently, struggles to reach the thermostat setting, or produces hot air at the unit but cool air at the registers may be dealing with duct restrictions or a ventilation issue. In that situation, troubleshooting furnace not heating properly includes both the mechanical components and the air path that carries heat around the house.
Why Clearing Blocked Vents And Ducts Improves Furnace Performance
Clearing vents and ducts does more than improve comfort. It also protects the furnace from unnecessary strain. When vents are closed or blocked, static pressure inside the ductwork rises. The blower has to work harder to move the same amount of air, which can shorten motor life and reduce overall efficiency. Over time, this extra stress can contribute to breakdowns or overheated components.
Cold spots and inconsistent temperatures are useful clues. If one bedroom is always colder than the rest of the house, start by confirming that the supply vent is fully open and that the return air path is not blocked by furniture. Light dust on vent grilles is normal, but heavy lint and debris can be vacuumed away to improve airflow. If several vents feel weak while the furnace itself seems to run normally, there may be a duct leak, disconnection, or heavy internal dust that calls for professional inspection and cleaning.
In addition, make sure interior doors are not constantly closed in a way that prevents air from circulating back to the main return. A heating system is designed with a specific airflow pattern in mind. Anything that disrupts that loop can make the home feel uneven and push the furnace to run longer than necessary.
How To Detect And Address Unusual Furnace Noises Or Smells
Unusual sounds or odors often appear at the same time as airflow problems and are important to take seriously. Rattling or buzzing near the blower compartment can suggest a loose panel, fastener, or duct connection. Banging when the furnace starts or stops may point to expanding and contracting ductwork, or in some cases, delayed ignition, which needs prompt professional attention.
Listen for changes over several heating cycles. A gentle hum and a soft rush of air are normal. Sharp metallic noises, grinding, or loud squeals are not and may signal a failing motor, worn bearings, or a blower wheel that is out of balance. These issues affect airflow and, if ignored, can lead to a complete loss of heat.
Smells can also help with troubleshooting furnace not heating problems. A slight dusty odor at the first start of the season is usually normal as dust burns off the heat exchanger. Persistent burning smells, smoke, or a hot electrical odor are different and should be treated as warning signs. If you notice those, turn the furnace off and have it inspected. Any suspicion of gas or a carbon monoxide alarm sounding calls for immediate evacuation and professional help rather than further investigation on your own.
By paying attention to airflow, noises, and smells together, you can often spot early signs of trouble and address simple causes, such as blocked vents, before they turn into costly repairs or uncomfortable nights without heat.
When Should You Call a Professional HVAC Technician For Furnace Repair?

There is a limit to what you can safely handle on your own when you are troubleshooting furnace not heating problems. Simple checks, such as confirming the thermostat setting, replacing a dirty filter, or resetting a tripped breaker, are usually safe for most homeowners. Once you move beyond those basics, however, the risks increase. Gas leaks, electrical faults, and internal mechanical failures can all turn into serious safety issues if they are not handled correctly.
As a general rule, if your furnace still will not produce consistent heat after you have worked through basic troubleshooting steps, or if you feel uncertain about what you are seeing or hearing, it is time to involve a professional. A licensed HVAC technician has the tools, training, and safety procedures needed to diagnose the system without putting your household at risk. This is especially important during very cold weather, when a furnace failure can quickly become more than just an inconvenience.
What Are The Warning Signs That Require Emergency Furnace Repair?
Some warning signs call for more than routine attention and should be treated as potential emergencies. A strong smell of gas anywhere near the furnace or gas line is one of the most serious. If you notice that odor, you should leave the home, avoid using electrical switches, and contact your gas company or emergency services from a safe location. You should not continue troubleshooting furnace not heating issues in that situation, because safety has to come first.
Other red flags include loud or sudden mechanical noises, such as banging, screeching, or grinding sounds that start when the furnace turns on. Repeated burner failures, flames that appear yellow instead of steady blue, or signs of scorching or smoke around the unit also point to conditions that need immediate professional evaluation. If your carbon monoxide detector alarms, or if family members experience headaches, dizziness, or nausea while the furnace is running, shut the system down and seek help right away. These are all signs that your heating equipment is not operating safely and should not be used until it has been inspected.
How Ace Tech HVAC Provides Fast And Reliable Heating System Repair In Metro Atlanta
When a problem goes beyond basic user checks, it helps to have a trusted local team to call. Ace Tech HVAC is a Georgia-based HVAC contractor that serves homeowners and businesses throughout Metro Atlanta. Their technicians work with a wide range of gas and electric furnaces, which means they are familiar with common regional issues such as heavy use during sudden cold snaps, older ductwork, and the impact of local power interruptions on modern equipment.
A typical visit starts with a focused diagnostic process that looks at thermostat communication, electrical supply, safety switches, ignition systems, and airflow. From there, the technician can explain what is causing the lack of heat, outline repair options, and recommend any preventive steps that may help avoid another breakdown later in the season. For many homeowners, this blend of technical expertise and clear communication is what turns a stressful no-heat situation into a manageable repair.
By combining careful DIY checks with timely professional support when warning signs appear, you can keep your furnace operating safely and efficiently through the winter and reduce the chances of an unexpected outage when you need heat the most.
Conclusion
A furnace that won’t heat is more than an inconvenience on a cold Atlanta night—it’s a sign that your system needs immediate professional attention. While checking your thermostat and filter are good first steps, persistent issues like a faulty ignitor or blower motor require expert diagnosis and repair. For fast, reliable service that restores your warmth and peace of mind, trust the certified furnace technicians at Ace Tech Heating & Cooling. Don’t spend another night shivering. Call (404) 369-9100 or get a free quote through our site form today for prompt furnace repair. Let’s get your heat back on.